Cloud Computing vs. Edge Computing: Which Is Best for Your Business?
August 2, 2023
Aron Wagner
CEO & Co-Founder
Digital data is growing at a phenomenal rate! The International Data Corporation (IDC) predicts that worldwide data will grow at an annual rate of 61% to 175 zettabytes by 2025.
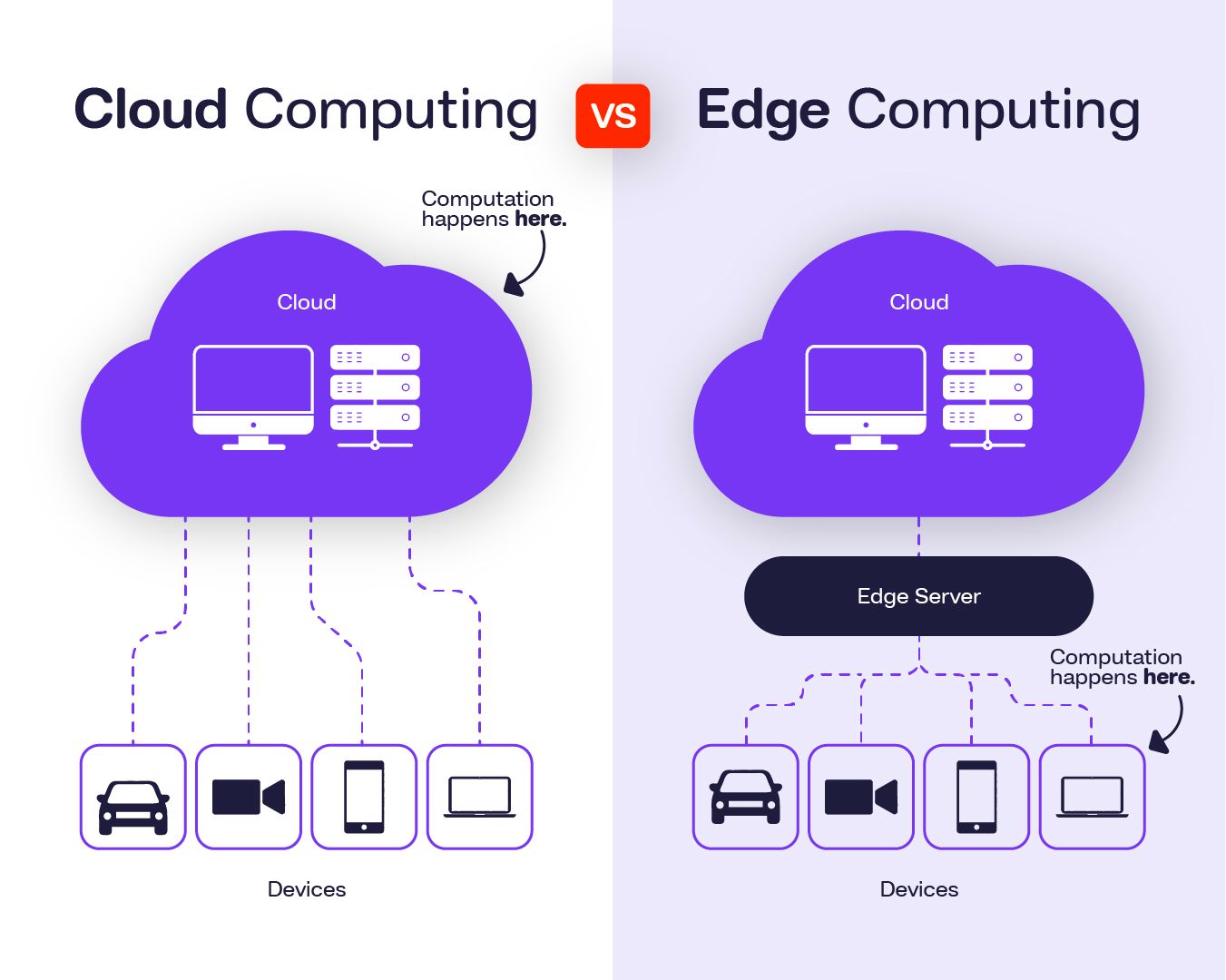
Businesses thrive on this data to leverage valuable insights and optimize their decision-making processes. The type of computing environment a business uses determines requirements around data storage needs, latency, and processing power. Cloud computing and edge computing are data network environments that serve distinctive needs and are often utilized in complement to each other.
Cloud Computing
The market size of the cloud computing industry stood at over $545 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of over 14% from 2023 to 2030. Key strengths include:
- Unlimited Storage — Cloud computing lets you store, access, and retrieve data easily with high storage capacities.
- Mobility and Accessibility — Cloud applications can be used anywhere and anytime with a simple internet connection.
- Cost-saving — Companies benefit from cutting down on upfront hardware expenses and overhead maintenance costs.
- Business Scalability — Cloud technology allows companies to rapidly expand by adjusting cloud storage according to business needs.
Edge Computing
Edge computing's market size is valued at over $13.50 billion in 2023 and is set to boom with the emergence of 5G, IoT, and AI-enabled technologies. Key benefits include:
- Improved Security — Enterprises can minimize security risks by staying in an offline computing environment instead of data transmission over the internet.
- Better for Compliance — Edge computing makes compliance easier by storing data locally and ensuring data sovereignty.
- Real-time Analysis of Data — Companies benefit from cutting down on lag time and improving quick decision-making. Autonomous vehicles and medical imaging require instantaneous data movement.
- Latency Reduction — Moving the compute point closer to the origin of data eliminates the need to move data from endpoints to a centralized cloud system.
Edge versus Cloud: Emerging Industry Trends
Edge computing has gained traction in healthcare IoT (real-time monitoring of temperatures for cold-storage supply chains), autonomous vehicles (interpreting traffic signals and road conditions with low latency), and augmented reality.
Cloud computing continues as the standard for storing and managing data, enabling team collaboration through services like Microsoft Teams and Google Drive, providing large-scale data storage for AI/ML enterprises, and driving productivity.
A Hybrid Future: Mixed Approaches
Business decisions about edge or cloud computing are unlikely to be binary. The circular nature of both technologies means they are not mutually exclusive. Cloud computing brings data together to provide analytical insights, which in turn get distributed over edge networks. The right combination of cloud and edge technologies is key to maximizing security, cost-efficiency, and revenue growth.
American Cloud Is at Your Service
American Cloud is an innovative cloud services provider focused on enhancing business agility and productivity. We offer multi-service cloud options ranging from web hosting and SaaS to mobile app development — all reliable and cost-effective.